Bread is a staple food in many households, but once it starts to get hard or dry, many people are unsure whether it’s still safe or healthy to eat. While the texture and taste of stale bread may not be as pleasant as when fresh, there’s a big difference between stale bread and spoiled or moldy bread—and understanding that difference can help reduce food waste and protect your health.
🍞 What Does “Stale” Really Mean?
“Stale” refers to bread that has lost moisture and become dry or hard. It doesn’t necessarily mean the bread is unsafe. In fact, staling is a natural process that begins as soon as bread cools after baking. During this process:
- The starch molecules in the bread recrystallize, causing the bread to become firm.
- The moisture migrates from the inner crumb to the crust and eventually evaporates.
According to a study in the Journal of Food Science (2007), staling is a reversible change—a slice of stale bread can often be revived by lightly heating or toasting it.
✅ Is It Safe to Eat Stale Bread?
Yes, stale bread is generally safe to eat, as long as:
- There is no mold (visible or hidden).
- It smells normal (no sour, musty, or “off” odor).
- It has been stored properly (in a clean, dry place or frozen soon after baking).
In fact, stale bread is commonly repurposed in cuisines around the world for delicious dishes like:
- French toast
- Bread pudding
- Croutons
- Stuffing
- Breadcrumbs
🚫 When Should You Avoid Stale Bread?
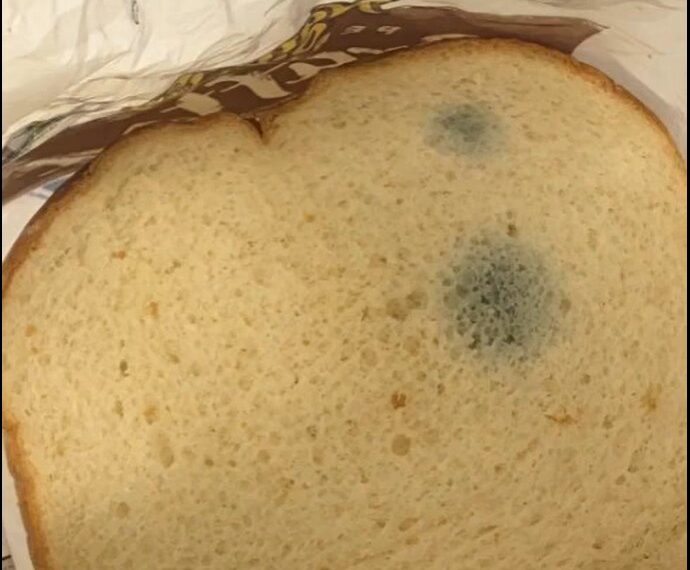
The real concern with bread isn’t staling—it’s mold.
❗ Mold on Bread: A Serious Health Risk
Bread is a high-risk food for mold growth because of its moisture content and carbohydrate base. Mold can appear in shades of green, white, blue, or even pink, and it often grows in warm, humid conditions.
- Mycotoxins, produced by some molds (especially Aspergillus and Penicillium species), can be toxic to humans and animals.
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO), mycotoxins can cause digestive issues, liver damage, and in some cases, may even be carcinogenic.
Unlike hard cheeses or firm vegetables, mold roots can spread quickly through the soft, porous structure of bread, even if you don’t see it on the surface.
👉 Bottom line: If you see or suspect mold on bread, throw it out immediately.
🧠 Nutritional Value: Does Stale Bread Lose Nutrients?
Stale bread retains most of its nutritional value, especially if it’s consumed within a few days of baking. However, over time:
- Vitamins like B1 (thiamine) can slowly degrade when exposed to air and light.
- Whole grain breads with seeds or fats may go rancid faster than white bread.
But overall, the difference is minor unless the bread has gone bad due to time or poor storage.
💡 How to Use and Store Stale Bread Safely
To make the most of stale bread:
TO CONTINUE READING THE ARTICLE PLEASE SEE PAGE 2