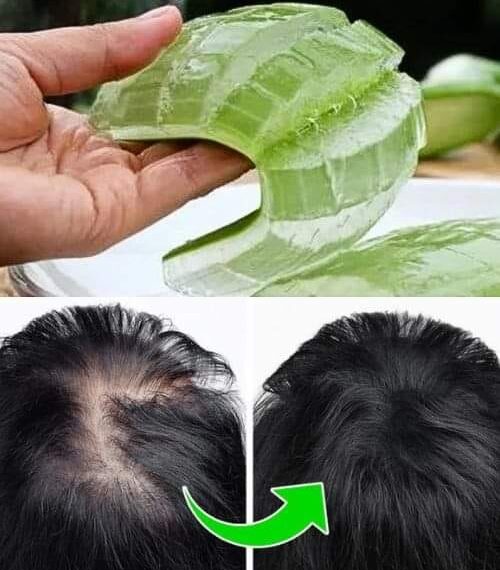
Aloe vera has been treasured for millennia — from ancient Egypt to modern skincare aisles — for its healing, soothing, and revitalizing properties. Its thick, spiky green leaves conceal a gel that’s packed with bioactive compounds, vitamins, enzymes, and antioxidants. The ancient Egyptians revered it so deeply that they called it the “Plant of Immortality,” and even used it in burial rituals and for embalming.
But what exactly does Aloe vera do to your body, and why does modern science support many of these ancient beliefs? Let’s explore the facts, health benefits, studies, and safe uses of this extraordinary plant.
🌱 A Glimpse into History
- Ancient Egyptians (circa 3000 BC) used Aloe vera for treating wounds, infections, and skin problems.
- Cleopatra is believed to have used it as part of her daily beauty routine.
- The Greeks called it the “universal panacea” and used it to treat baldness and insomnia.
- In traditional Ayurveda and Chinese medicine, Aloe is used to treat fungal diseases, fever, and digestive problems.
🧪 What’s Inside Aloe Vera Gel?
Aloe vera contains over 75 active compounds, including:
- Vitamins A, C, E (antioxidants), B12
- Enzymes (e.g., bradykinase – reduces inflammation)
- Minerals (calcium, magnesium, zinc, selenium)
- Saponins (natural antiseptic)
- Amino acids (including 7 of the 8 essential ones)
- Polysaccharides (e.g., acemannan – boosts immune response)
✅ Health Benefits of Aloe Vera: What It Does to Your Body
1. Heals Skin Faster
Aloe is widely used for:
- Sunburns
- Cuts and scrapes
- Acne scars
- Eczema and psoriasis
📚 Study: A clinical review in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology (1999) confirmed Aloe vera’s ability to speed up wound healing by increasing collagen synthesis and blood flow to the area.
2. Soothes Inflammation and Reduces Pain
Thanks to compounds like bradykinase, Aloe has natural anti-inflammatory properties. Applied topically or consumed (in limited quantities), it helps:
- Reduce joint pain and arthritis symptoms
- Soothe skin inflammation
- Calm gut irritation
🔬 Research: A 2014 study in Phytomedicine found Aloe extract effective in reducing symptoms in patients with osteoarthritis.
3. Supports Digestive Health
When taken orally in controlled amounts, Aloe vera juice can:
- Act as a natural laxative
- Alleviate constipation
- Reduce symptoms of IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)
- Soothe acid reflux and gastritis
⚠️ Warning: The latex (yellow part under the leaf skin) contains aloin, a potent laxative, and should be avoided in large doses.
📘 Study: A randomized controlled trial published in Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics (2004) found that Aloe vera extract helped reduce symptoms in patients with ulcerative colitis.
4. Boosts Immune System
Aloe contains acemannan, a polysaccharide that enhances white blood cell activity, helping your body fight off infections.
📊 Fact: Acemannan stimulates macrophages (immune cells) to produce cytokines, which are crucial for immune defense.
🌼 Beauty & Skin Uses
TO CONTINUE READING THE ARTICLE PLEASE SEE PAGE 2